Console prompts¶
In addition to console abstraction layer Zend Framework 2 provides numerous convenience classes for interacting with the user in console environment. This chapter describes available Zend\Console\Prompt classes and their example usage.
All prompts can be instantiated as objects and provide show() method.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | use Zend\Console\Prompt;
$confirm = new Prompt\Confirm('Are you sure you want to continue?');
$result = $confirm->show();
if ($result) {
// the user chose to continue
}
|
There is also a shorter method of displaying prompts, using static prompt() method:
1 2 3 4 5 6 | use Zend\Console\Prompt;
$result = Prompt\Confirm::prompt('Are you sure you want to continue?');
if ($result) {
// the user chose to continue
}
|
Both of above examples will display something like this:
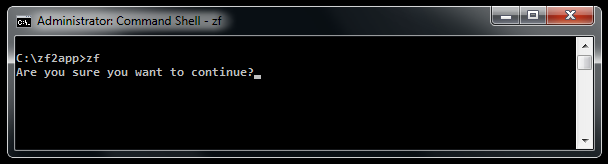
See also
Make sure to read about console MVC integration first, because it provides a convenient way for running modular console applications without directly writing to or reading from console window.
Confirm¶
This prompt is best used for a yes / no type of choices.
Confirm( string $text, string $yesChar = 'y', string $noChar = 'n' )
- $text
- (string) The text to show with the prompt
- $yesChar
- (string) The char that corresponds with YES choice. Defaults to y.
- $noChar
- (string) The char that corresponds with NO choice. Defaults to n.
Example usage:
use Zend\Console\Prompt\Confirm;
if ( Confirm::prompt('Is this the correct answer? [y/n]', 'y', 'n') ) {
$console->write("You chose YES");
} else {
$console->write("You chose NO");
}
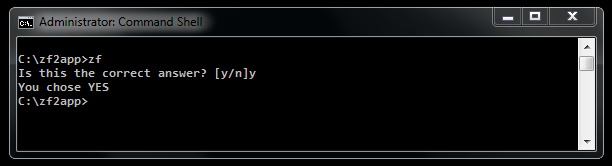
Line¶
This prompt asks for a line of text input.
Line(
string $text = 'Please enter value',
bool $allowEmpty = false,
bool $maxLength = 2048
)
- $text
- (string) The text to show with the prompt
- $allowEmpty
- (boolean) Can this prompt be skipped, by pressing [ENTER] ? (default fo false)
- $maxLength
- (integer) Maximum length of the input. Anything above this limit will be truncated.
Example usage:
use Zend\Console\Prompt\Line;
$name = Line::prompt(
'What is your name?',
false,
100
);
$console->write("Good day to you $name!");
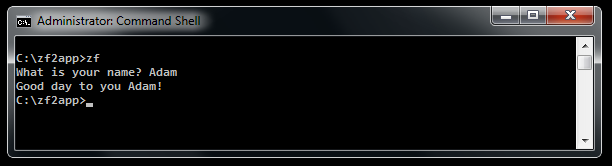
Char¶
This prompt reads a single keystroke and optionally validates it against a list o allowed characters.
Char(
string $text = 'Please hit a key',
string $allowedChars = 'abc',
bool $ignoreCase = true,
bool $allowEmpty = false,
bool $echo = true
)
- $text
- (string) The text to show with the prompt
- $allowedChars
- (string) A list of allowed keys that can be pressed.
- $ignoreCase
- (boolean) Ignore the case of chars pressed (default to true)
- $allowEmpty
- (boolean) Can this prompt be skipped, by pressing [ENTER] ? (default fo false)
- $echo
- (boolean) Should the selection be displayed on the screen ?
Example usage:
use Zend\Console\Prompt\Char;
$answer = Char::prompt(
'What is the correct answer? [a,b,c,d,e]',
'abcde',
true,
false,
true
);
if ($answer == 'b') {
$console->write('Correct. This it the right answer');
} else {
$console->write('Wrong ! Try again.');
}
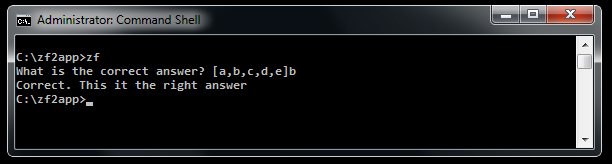
Select¶
This prompt displays a number of choices and asks the user to pick one.
Select(
string $text = 'Please select one option',
array $options = array(),
bool $allowEmpty = false,
bool $echo = false
)
- $text
- (string) The text to show with the prompt
- $options
- (array) An associative array with keys strokes (chars) and their displayed values.
- $allowEmpty
- (boolean) Can this prompt be skipped, by pressing [ENTER] ? (default fo false)
- $echo
- (boolean) Should the selection be displayed on the screen ?
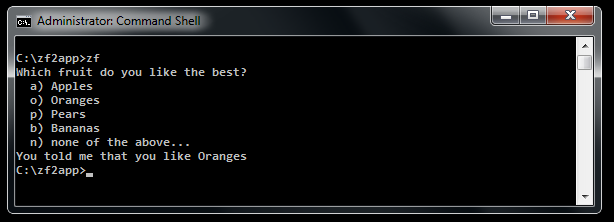
Example usage:
$options = array(
'a' => 'Apples',
'o' => 'Oranges',
'p' => 'Pears',
'b' => 'Bananas',
'n' => 'none of the above...'
);
$answer = Select::prompt(
'Which fruit do you like the best?',
$options,
false,
false
);
$console->write("You told me that you like " . $options[$answer]);
See also
To learn more about accessing console, writing to and reading from it, make sure to read the following chapter: Console adapters.
